What Are 3 General Nutrition Recommendations On Fat?
When it comes to incorporating fats into a balanced diet, you might be wondering, “What are 3 general nutrition recommendations on fat?”
As per our expertise, the top dietitian advice centers around adding healthy fats to your diet, understanding how to read labels for fat content, and knowing which fats to prioritize.
At Berry Street, we make it easy to connect with a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist to help you create sustainable eating habits that suit your unique wellness goals.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essentials of dietary fats, understanding heart-friendly options, and learning how to read labels effectively to curate a nutritious diet and lifestyle.
What Are 3 General Nutrition Recommendations On Fat?
We’ve curated our top three dietitian recommendations on fat and how to incorporate them easily and safely into your diet and lifestyle.
1. Add Healthy Sources Of Dietary Fats To Regular Meals
Based on our first-hand experience, healthy unsaturated fats play a significant role in your overall well-being, providing energy and supporting cell function.
Unlike saturated and trans fats, unsaturated fats don’t raise harmful cholesterol levels. In fact, many dietary fats offer protective benefits for your heart and replenish the body’s energy needs.
Additionally, for anyone wondering, "Do dietitians make meal plans?", the answer is yes. A Registered Dietitian can design a unique meal plan that includes appropriate types and portions of dietary fats.
Plant Sterols Can Lower Cholesterol
Phytosterols, found in vegetables, nuts, and seeds, naturally help reduce cholesterol by blocking its absorption in our intestines. These plant sterol compounds mimic cholesterol's structure, replacing it in the digestive system.
Fatty Acids Are Essential In Your Diet
Our research indicates that fatty acids, particularly omega-3 and omega-6, are essential for brain wellness, immune function, and cell structure.
You can’t produce these acids naturally, so you must obtain them from your diet. By adding fish like salmon, chia seeds, as well as ground flaxseeds or flaxseed oil to your diet, you can boost omega-3 intake easily.
Need guidance on consuming healthy fats in your diet? Chat with a Registered Dietitian covered by insurance at Berry Street today for personalized meal advice!

2. Consume Heart-Healthy Fats
According to the Cochrane Heart Group, heart-healthy fats can reduce inflammation and lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.
One of the many benefits of seeing a dietitian, like a heart health dietitian, is gaining insights into how best to incorporate these types of fats into your regular meals.
Let’s take a closer look at two heart-healthy fats: monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats.
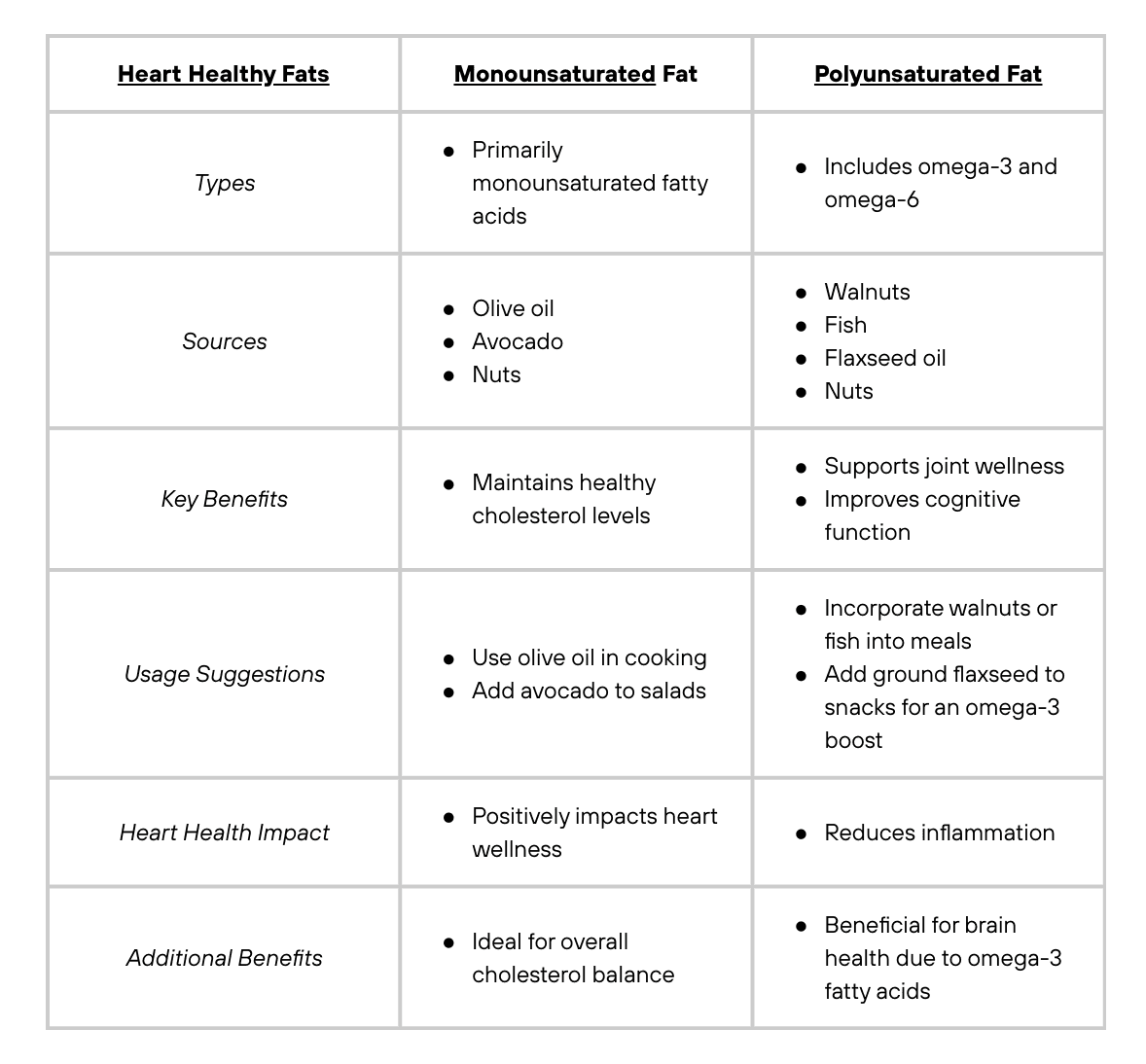
Monounsaturated Fat
Monounsaturated fats are heart-healthy and encourage various aspects of wellness. Usually found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts—they’re ideal for conserving stable cholesterol levels.
Based on our observations, using olive oil in cooking or adding avocado to salads can promote the wellbeing of your heart by positively impacting your cholesterol levels.
Polyunsaturated Fat
Polyunsaturated fats provide omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, essential for joint and cognitive health. Found in sources like fish, walnuts, and flaxseed oil, they can reduce inflammation, which benefits cardiovascular wellness.
After putting it to the test, we saw that consuming these fats supports joint health and improves cognitive function. Additionally, you can place a handful of walnuts in your favorite daily snack for an omega-3 boost.
3. Learn To Read How Fats Are Listed On Product Labels
Understanding fat content on labels is essential for making informed dietary choices.
At Berry Street, our virtual Registered Dietitians and Certified Nutrition Specialists will recommend that you take a closer look at ‘total fats’, ‘trans fats’, and ‘saturated fats’ on nutrition labels.
One advantage of working with a dietitian vs doctor for dietary advice is that Registered Dietitians have specialized training in nutrition label reading.
This can make grocery shopping simpler and more effective for you, as doctors tend to only have a general knowledge of nutrition as a whole (unless they specialize specifically in this area of medicine).
Here are a few more questions you need to ask yourself when reading product labels.

Do All Fats Have The Same Number Of Calories?
Each gram of fat contains approximately nine calories. They’re more calorie-dense than proteins or carbohydrates, which contain about four calories per gram.
Drawing from our experience, watching serving sizes and calorie intake can help manage your dietary fat consumption effectively.
Are All Foods Labeled “Trans Fat-Free” Healthy Foods?
Not all foods marked “trans fat-free” are healthy.
That’s why it’s critical to check the ingredients list for “partially hydrogenated oils”, which is a good indicator of any hidden, harmful trans fats in certain products.
Foods that are labeled as “trans fat free” may still contain high levels of sugar, sodium, or other unhealthy ingredients.
A Registered Dietitian online consultation at Berry Street can give you a better understanding of nutrition labels—making food shopping and meal planning stress free!
Fat And Cholesterol FAQs
How Many Different Kinds Of Fats Are There?
There are four primary types of fats:
monounsaturated fats
polyunsaturated fats
saturated fats
trans fats
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are beneficial when consumed in moderation, whereas the Mayo Clinic recommends avoiding eating trans fats and lowering consumption of saturated fats to a daily intake of less than 10%.
Our findings show that different types of dietitians as well as types of nutritionists specialize in helping you understand these dietary nuances for improved meal planning.

What's The Difference Between Saturated And Unsaturated Fats?
Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature and found in animal products and coconut, while unsaturated fats are liquid and primarily found in plant-based sources.
Saturated fats raise what's known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or 'bad cholesterol' levels in the body. In contrast, unsaturated fats often contain lower LDL and higher amounts of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or 'good cholesterol' to help you preserve healthy cholesterol levels.
How Much Fat Should Kids Get?
For children, KidsHealth asserts that daily caloric intake of approximately 25-35% of healthy dietary fats are essential for their overall growth and brain development.
As such, our pediatric dietitians suggest focusing on healthy sources of dietary fats like avocados and nuts in this regard. Moreover, you shouldn’t be afraid to give your children whole-milk dairy, it’s actually recommended by dietetics experts once an infant turns one year old.
How Can I Keep Fats Under Control?
To control fat intake, choose healthier cooking methods like grilling, baking, or steaming, and limit fried foods.
Incorporate healthy oils, such as olive or avocado oil, while planning meals containing appropriate portions of fats (20-35%), proteins (10–35%), and carbs (45–65%).
This approach supports a nutritious diet and makes it easier to monitor fat consumption while maintaining your weight without compromising flavor or nutrition.
Working with the best dietitian for weight loss, such as a dietitian weight loss expert, can help you monitor your fat consumption without feeling deprived.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we found that three general recommendations from dietitians on fat consumption encompasses adding healthy fats to meals, prioritizing heart-healthy options, and understanding nutrition labels.
At Berry Street, we’re here to connect you with experienced dietitians who understand your individual needs and can help you make mindful choices when consuming healthy fats in your diet.
Ready to start? Reach out today to work with the best licensed 'dietitians and nutritionists near me' and achieve optimal wellness!