Intermittent fasting is more than just skipping meals—it’s a structured approach to eating that can support weight management, metabolic health, and overall well-being. An intermittent fasting diet plan focuses on when to eat rather than what to eat, making it a flexible option for many lifestyles.
There are several fasting methods, but the 16/8 approach is one of the most popular and sustainable. Choosing nutrient-dense foods during eating windows is essential to feeling full and energized, and a well-balanced meal plan makes the process easier.
After putting intermittent fasting to the test, we’ve created a simple 7-day meal plan, outlined key benefits, and shared essential tips to help make fasting safe and effective.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is an eating pattern that alternates between fasting and eating windows. The most common approach is the 16/8 method, where you fast for 16 hours and eat within an 8-hour window.
According to our research, the 16/8 method is the easiest to maintain and integrate into a routine, especially when compared to a detox meal plan.
What Foods Should You Eat While Intermittent Fasting?
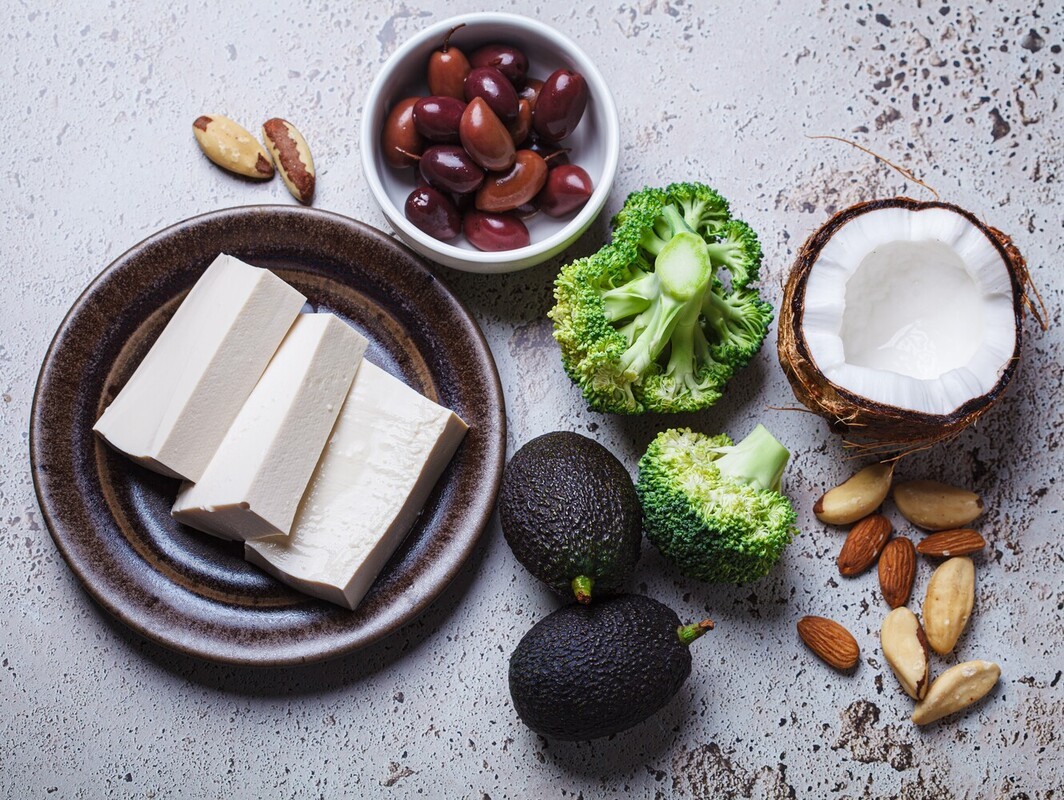
Intermittent fasting isn’t just about skipping meals—it’s about maximizing nutrition during your eating window. To feel satisfied and support your health, focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods.
Best Foods For Intermittent Fasting
Proteins: Eggs, lean meats, poultry, fish, tofu, lentils, beans
Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, coconut oil
Fiber-Rich Carbohydrates: Quinoa, brown rice, whole grains, starchy vegetables
Fruits And Vegetables: Leafy greens, berries, carrots, bell peppers, tomatoes
Beverages: Water, herbal teas, black coffee (no sugar), bone broth
Foods To Avoid
Processed foods (packaged snacks, fast food)
Sugary beverages (soda, sweetened coffee drinks)
Excess refined carbs (white bread, pastries, white pasta)
Fried foods and trans fats
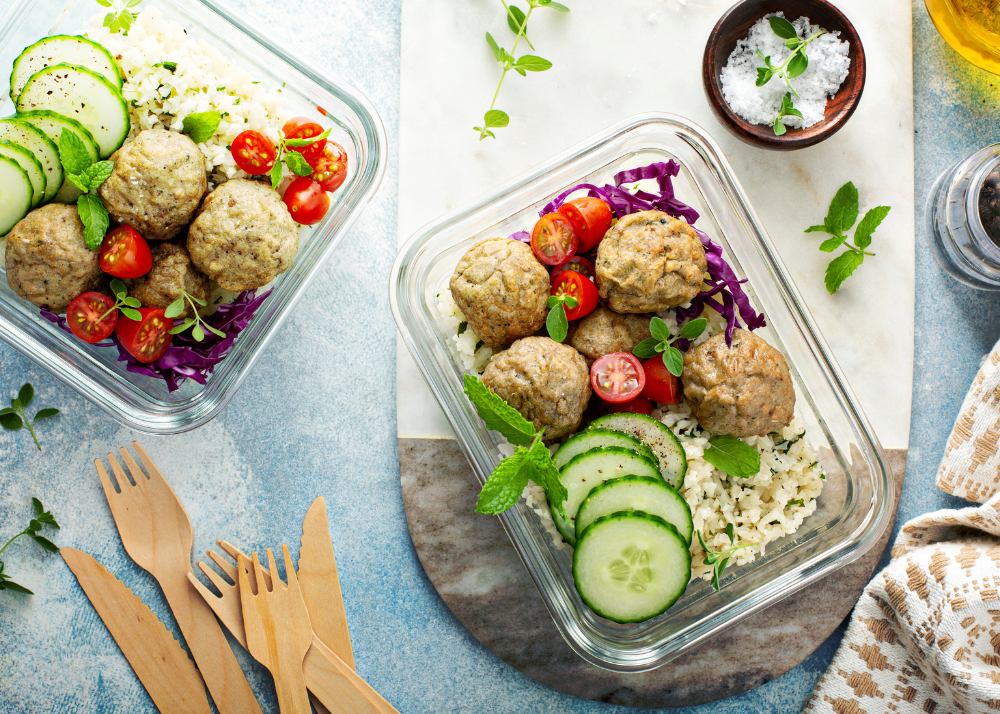
7-Day Intermittent Fasting Meal Plan
This 7-day meal plan follows the 16/8 intermittent fasting approach, with an eating window from 12:00 PM to 8:00 PM. Each meal is packed with nutrients to keep you full, energized, and satisfied. Feel free to adjust meal timings based on your preferences and lifestyle.
Day 1
Breakfast (12:00 PM): Scrambled eggs with avocado and whole-grain toast
Snack (3:00 PM): Greek yogurt with almonds and berries
Lunch (5:30 PM): Grilled chicken salad with quinoa and olive oil dressing
Dinner (7:30 PM): Salmon with roasted sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli

Day 2
Breakfast: Oatmeal with peanut butter and banana
Snack: Hard-boiled eggs and hummus with cucumber slices
Lunch: Spicy turkey meatballs with roasted veggies
Dinner: Thai beef lettuce wraps
Day 3
Breakfast: Spinach and cheese omelet with a whole-grain wrap
Snack: Apple slices with almond butter
Lunch: Grilled chicken with brown rice and sautéed greens
Dinner: Italian meatball soup
Day 4
Breakfast: Chia pudding with walnuts and cinnamon
Snack: Cottage cheese with berries and pistachios
Lunch: Chicken fajita bowl with quinoa
Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted cauliflower
Day 5
Breakfast: Avocado toast with poached eggs
Snack: Roasted chickpeas with turmeric
Lunch: Lentil soup with a mixed greens salad
Dinner: Grilled steak with mashed sweet potatoes
Day 6
Breakfast: Protein smoothie with almond milk, banana, and flaxseeds
Snack: Dark chocolate and nuts
Lunch: Mediterranean quinoa bowl with feta cheese and chickpeas
Dinner: Baked cod with roasted zucchini and garlic butter
Day 7
Breakfast: Greek yogurt with granola and berries
Snack: Boiled eggs with avocado slices
Lunch: Vegetable stir-fry with tofu and brown rice
Dinner: Chicken tortilla soup with a side salad

Improves Blood Sugar Control
Fasting periods allow insulin levels to drop, helping to improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation. Lower insulin levels reduce the risk of insulin resistance, which is a key factor in developing type 2 diabetes.
Studies suggest that intermittent fasting may help stabilize blood sugar levels, making it a promising approach for those at risk of metabolic disorders. However, people with diabetes or other medical conditions should consult a healthcare provider before trying fasting.
Supports Heart Health
Heart disease risk factors such as high cholesterol, inflammation, and high blood pressure can improve with intermittent fasting. Studies indicate that fasting may help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides while maintaining or even increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
Fasting has also been shown to reduce markers of inflammation, which plays a role in heart disease development. By supporting metabolic health, intermittent fasting may contribute to better cardiovascular function over time.
Is Intermittent Fasting Safe?
For most healthy adults, intermittent fasting is a safe and effective way to support overall health. However, it’s not for everyone. Pregnant or nursing individuals, those who are underweight, or people with a history of eating disorders should avoid fasting.
If you have diabetes, low blood pressure, or any other medical condition, it’s important to consult your doctor before starting. Listening to your body is key—if you feel weak, dizzy, or overly hungry, adjust your approach.
Everyone’s needs are different, and a personalized plan can make all the difference. Connect with a Registered Health Dietitian at Berry Street to create a customized 7-day intermittent fasting meal plan that fits your needs, lifestyle, and goals, whether you’re after a standard intermittent fasting diet plan or a vegan keto meal plan.
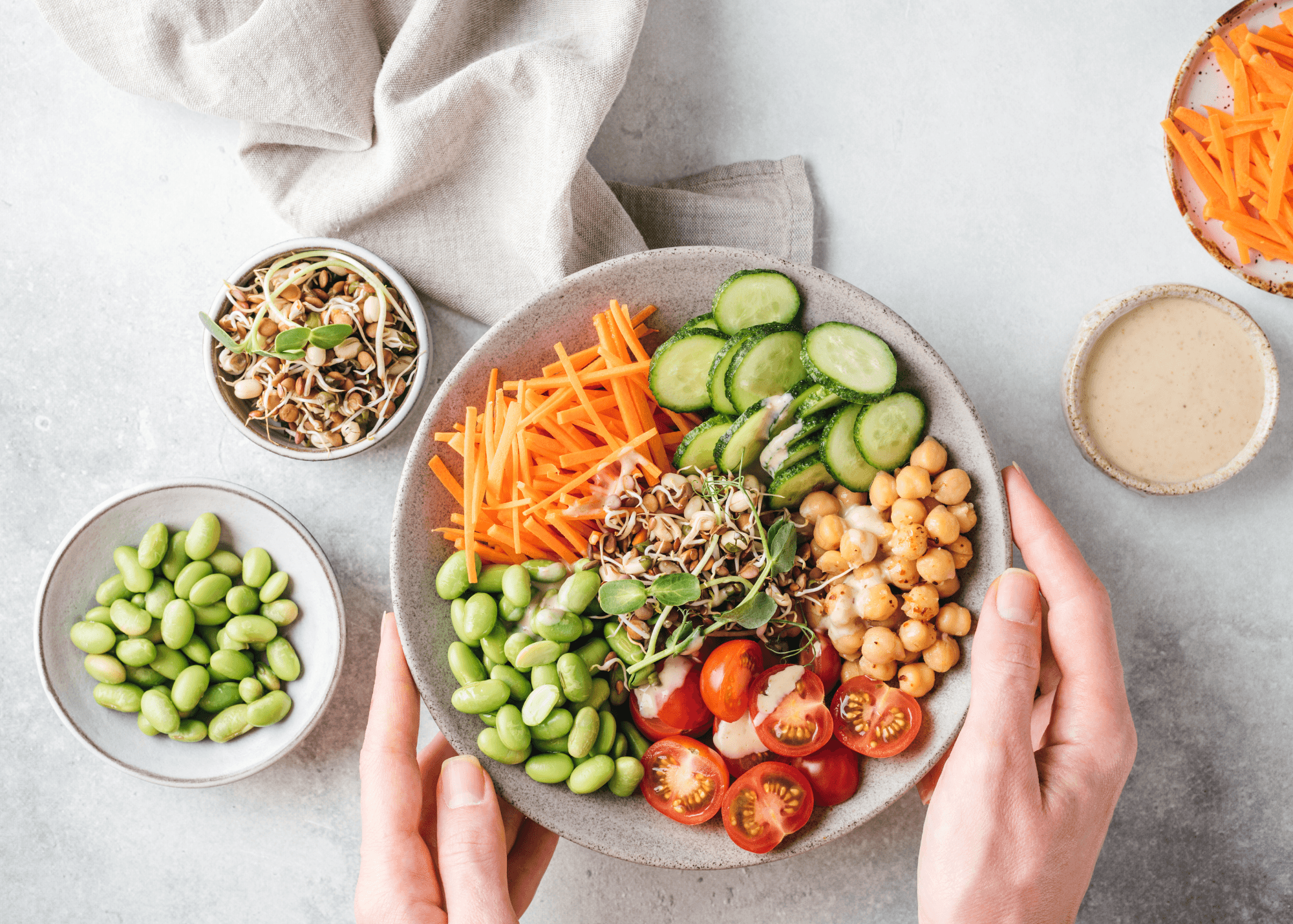

Tips For Safe And Effective Fasting
Intermittent fasting can be a tool for better health, but it’s important to do it in a way that supports your body’s needs. By following these key tips, fasting can become a sustainable and enjoyable part of your lifestyle:
Start Slowly
Jumping into long fasting periods too quickly can leave you feeling fatigued and frustrated. Instead, ease into intermittent fasting by gradually increasing your fasting window over a few weeks.
Start with a 12-hour fast and slowly work toward 14 or 16 hours as your body adapts. This approach helps minimize hunger, irritability, and energy crashes while allowing your metabolism to adjust naturally.
Stay Hydrated
Hydration is crucial while fasting, as your body still needs fluids to function properly. Drinking plenty of water can help curb hunger, support digestion, and prevent dehydration-related headaches.
In our experience, herbal teas and black coffee (without sugar or cream) are also fantastic options that won’t break your fast. If you’re feeling sluggish or lightheaded, adding a pinch of salt to your water can help replenish electrolytes and keep your body balanced.
Focus On Nutrient-Dense Meals
What you eat during your eating window matters just as much as when you eat. Prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods that include lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates.
These nutrients help stabilize blood sugar levels, keep you full longer, and prevent energy crashes. Skipping highly processed foods and excess sugar will make fasting easier and support better overall health.

Don’t Overeat In Your Eating Window
It can be tempting to eat large portions or indulge in unhealthy foods after a long fast, but overeating can lead to digestive discomfort and negate the benefits of fasting. Instead, focus on mindful eating by starting with a balanced meal and paying attention to hunger cues.
Eating slowly and choosing whole, satisfying foods will help prevent bloating, sluggishness, and unnecessary calorie intake.
Listen To Your Body
Intermittent fasting should work for you, not against you. If you feel overly fatigued, irritable, or experience frequent dizziness, your fasting window may be too long. Adjust your approach by shortening your fast, increasing your nutrient intake, or trying a different fasting method.
Everyone's body responds differently, so finding the right balance is key. If fasting ever feels overwhelming, it’s okay to take a step back and reassess. Your health and well-being always come first.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting is a flexible and effective way to support weight management, improve metabolic health, and boost overall well-being. Choosing the right fasting method, eating nutrient-dense meals, and staying hydrated are all key to making it work.
While intermittent fasting is generally safe, it’s important to listen to your body and adjust as needed. A well-planned approach can help you sustain this lifestyle without stress or deprivation.
If you’re ready to get started with a plan that fits your goals and daily routine, connect with a Registered Dietitian at Berry Street for expert guidance and a personalized 7-day intermittent fasting meal plan.
Intermittent Fasting Diet Plan (FAQs)
Can I exercise while intermittent fasting?
Yes! Many people workout in a fast state and see great results.
Light cardio or strength training is generally safe, but if you feel weak or lightheaded, try eating a small protein-rich snack before your workout. Post-workout meals should include protein and healthy carbs to aid recovery.
What can I drink during the fasting window?
Water, black coffee, herbal tea, and other non-caloric beverages are allowed and encouraged. Avoid anything with added sugars, cream, or artificial sweeteners, as they may trigger an insulin response and break your fast.
Will intermittent fasting slow down my metabolism?
No, intermittent fasting may actually support metabolic health by improving insulin sensitivity and increasing fat-burning efficiency. However, extreme calorie restriction for long periods can have the opposite effect, so it’s important to eat enough nutrient-dense foods during your eating window.